Gaining insight into average weather patterns is essential for planning daily activities, managing agriculture, enhancing travel experiences, and even predicting long-term climate shifts. Weather dynamics significantly influence human life, affecting health, safety, economic productivity, and beyond. Whether you're a farmer preparing for planting, a traveler selecting vacation spots, or someone keen to explore climate trends, understanding average weather provides meaningful perspectives.
Average weather refers to the typical atmospheric conditions in a particular location over an extended timeframe. These conditions encompass temperature, precipitation, wind speed, humidity, and additional meteorological factors. By analyzing these patterns, we can anticipate seasonal shifts and prepare for potential challenges more effectively.
This article delves deeply into the concept of average weather, its importance, and its impact on various aspects of life. Whether you're seeking to comprehend climate trends or explore practical applications, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the necessary information.
Read also:Exploring The Highest Salaries In The Wnba
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Basics of Average Weather
- Defining Average Weather
- Methods of Measuring Average Weather
- Understanding Seasonal Patterns in Average Weather
- Analyzing Global Trends in Average Weather
- The Influence of Climate Change on Average Weather
- Utilizing Tools and Resources for Tracking Average Weather
- Practical Applications of Average Weather Data
- Examining Regional Variations in Average Weather
- Forecasting Future Trends in Average Weather
Exploring the Basics of Average Weather
Average weather is instrumental in shaping our comprehension of the environment. It establishes a baseline for evaluating both short-term weather variations and long-term climate trends. Through the analysis of historical data, meteorologists can identify patterns that assist in predicting future conditions.
For instance, average weather data empowers farmers to determine the optimal planting times for crops, ensuring maximum growth and yield. Similarly, urban planners leverage this information to construct infrastructure capable of enduring extreme weather occurrences.
A deeper understanding of average weather also enhances disaster preparedness. By studying past weather patterns, communities can devise strategies to minimize the impact of natural calamities such as hurricanes, floods, and heatwaves.
Defining Average Weather
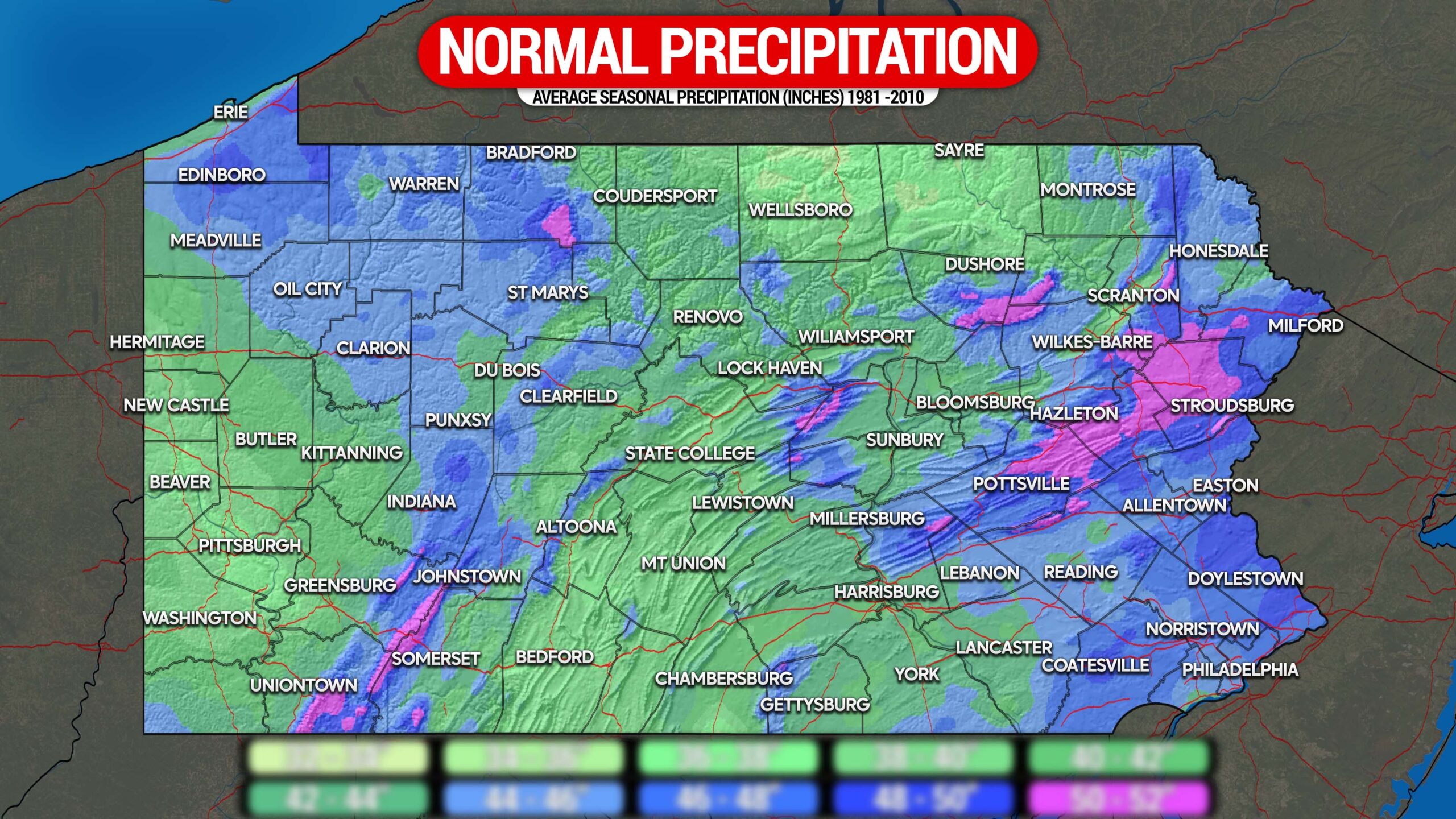
Average weather represents the typical atmospheric conditions experienced in a specific location over an extended timeframe, typically spanning 30 years. This duration is recognized as the climatological normal, as defined by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). During this period, meteorologists gather data on temperature, precipitation, wind speed, humidity, and other relevant factors to compute averages.
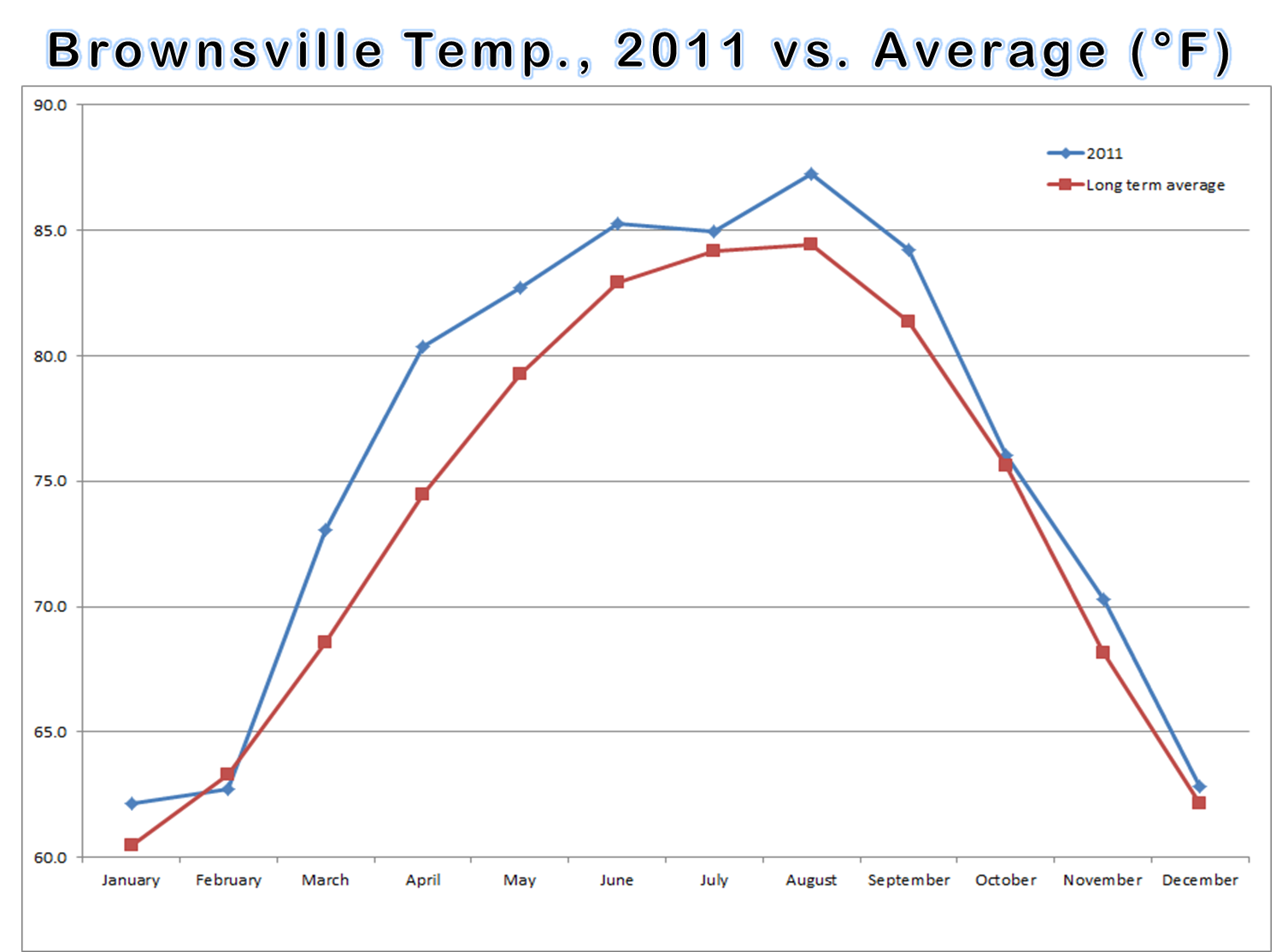
These averages offer a snapshot of expected weather conditions. For example, if the average July temperature in a city is 25°C, it signifies that over the past 30 years, July temperatures have consistently hovered around this value.
Key Components of Average Weather
- Temperature: The average temperature is calculated by averaging daily high and low temperatures over a specified timeframe.
- Precipitation: This encompasses rainfall, snowfall, and other forms of moisture. Average precipitation is determined by summing up the total rainfall over the years and dividing it by the number of years.
- Wind Speed: Average wind speed is measured using anemometers and calculated over a prolonged period for consistency.
- Humidity: Relative humidity levels are averaged to indicate the typical moisture content in the air of a specific location.
Methods of Measuring Average Weather
To measure average weather, meteorologists rely on an extensive network of weather stations equipped with advanced instruments. These stations continuously monitor atmospheric conditions and relay data to centralized databases for analysis.
Read also:Comprehensive Guide To Liga Mx 2024 Everything You Need To Know
The process involves collecting data over a 30-year period, dividing it into smaller intervals for detailed analysis. This ensures that the averages accurately reflect long-term trends while accounting for seasonal variations.
Advanced Technologies in Weather Measurement
- Satellites: Weather satellites provide real-time data on cloud cover, temperature, and precipitation patterns across vast regions.
- Radar Systems: Radar technology is utilized to track precipitation and storm systems, offering valuable insights into short-term weather patterns.
- Computer Models: Advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques are employed to process extensive data and generate precise predictions.
Understanding Seasonal Patterns in Average Weather
Seasonal patterns in average weather are driven by the Earth's rotation and tilt. These patterns vary significantly across different regions, leading to distinct climatic zones. For example, tropical regions experience relatively consistent temperatures year-round, while temperate zones exhibit distinct seasons with varying temperatures and precipitation levels.
Recognizing these patterns is crucial for planning and decision-making. For instance, businesses in the tourism industry heavily depend on seasonal weather patterns to attract visitors during peak periods.
Regional Seasonal Variations
- Tropical Regions: High temperatures and heavy rainfall during the wet season.
- Temperate Zones: Four distinct seasons characterized by varying temperatures and precipitation.
- Polar Regions: Extremely cold temperatures and limited daylight during the winter months.
Analyzing Global Trends in Average Weather
Over the past few decades, global trends in average weather have shown considerable changes. Rising temperatures, shifting precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events are notable examples of these changes. These trends are primarily attributed to human-induced climate change.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), global average temperatures have risen by approximately 1.1°C since the pre-industrial era. This increase has resulted in more frequent heatwaves, droughts, and heavy rainfall events worldwide.
Key Statistics on Global Trends
- Temperature Rise: Global average temperatures have increased by 1.1°C since the late 19th century.
- Precipitation Changes: Some regions have witnessed increased rainfall, while others have become drier.
- Sea Level Rise: Global sea levels have risen by about 8-9 inches since 1880, with the rate accelerating in recent years.
The Influence of Climate Change on Average Weather
Climate change profoundly impacts average weather patterns. As greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise, the Earth's atmosphere traps more heat, leading to a range of environmental changes. These changes affect not only average weather but also the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events.
For instance, regions that previously experienced moderate rainfall may now face prolonged droughts or heavy downpours. Similarly, coastal areas are increasingly vulnerable to sea level rise and storm surges.
Adapting to Climate Change
- Infrastructure Development: Constructing resilient infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events.
- Policy Implementation: Enforcing policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable practices.
- Community Engagement: Educating communities about the impacts of climate change and encouraging proactive measures.
Utilizing Tools and Resources for Tracking Average Weather
Various tools and resources are available for monitoring average weather patterns. These tools range from online platforms to mobile applications, offering real-time data and historical records.
One of the most popular resources is the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), which provides comprehensive datasets and analysis tools. Additionally, platforms like Weather.com and AccuWeather offer user-friendly interfaces for accessing weather information.
Recommended Tools
- NOAA Climate Data Online: Grants access to historical weather data and analysis tools.
- Weather.com: Supplies real-time weather updates and forecasts for numerous locations.
- AccuWeather: Provides detailed weather reports and interactive maps for tracking weather patterns.
Practical Applications of Average Weather Data
Average weather data has numerous practical applications across various industries. From agriculture to energy production, understanding weather patterns can lead to more efficient and sustainable practices.
In agriculture, farmers use average weather data to optimize planting schedules and resource allocation. Similarly, energy companies rely on weather forecasts to predict demand and adjust supply accordingly.
Industries Benefiting from Average Weather Data
- Agriculture: Planning crop cycles and managing water resources.
- Energy: Forecasting energy demand and adjusting production levels.
- Transportation: Ensuring safe and efficient operations during adverse weather conditions.
Examining Regional Variations in Average Weather
Regional variations in average weather are influenced by geographical factors such as latitude, altitude, and proximity to large bodies of water. These variations result in diverse climatic conditions worldwide.
For example, coastal regions often experience milder temperatures due to the ocean's moderating effect. In contrast, inland areas may encounter more extreme temperature fluctuations.
Examples of Regional Variations
- Coastal Regions: Cooler summers and warmer winters compared to inland areas.
- Mountainous Areas: Lower temperatures and higher precipitation levels at higher altitudes.
- Desert Regions: Extremely high temperatures during the day and cold nights due to low humidity.
Forecasting Future Trends in Average Weather
As climate change continues to reshape the planet, future predictions for average weather indicate significant shifts. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events are expected to become more prominent.
Scientists are utilizing advanced models and simulations to forecast these changes, providing valuable insights for policymakers and stakeholders. By understanding these predictions, communities can develop strategies to adapt and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Key Predictions for the Future
- Temperature Increase: Global average temperatures are projected to rise by 2-4°C by the end of the century.
- Precipitation Changes: Some regions may experience increased rainfall, while others face prolonged droughts.
- Extreme Events: More frequent and intense heatwaves, hurricanes, and floods are anticipated in many parts of the world.
Kesimpulan
In summary, understanding average weather is crucial for planning and decision-making in various aspects of life. From agriculture and energy production to disaster preparedness and climate adaptation, this knowledge offers valuable insights for addressing current and future challenges.
We encourage readers to explore the tools and resources mentioned in this article to gain a deeper understanding of average weather patterns. By staying informed and proactive, we can better prepare for the impacts of climate change and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.
Feel free to leave a comment or share this article with others who might find it useful. For more information on related topics, explore our other articles on climate and environmental issues.